An animal that has been sick over a longer period of time runs the risk of having the.
What causes laminitis in cattle.
1 department of veterinary anesthesiology radiology and surgery western college of veterinary medicine university of saskatchewan saskatoon canada.
Laminitis in dairy cattle.
Antihistamines may be useful e g.
Laminitis in feedlot cattle is associated with a rapid increase in highly digestible carbohydrates grain in the diet which changes the acidity in the rumen and in turn kills off some types of digestive organisms that release toxins into the bloodstream as they die.
Laminitis is regarded as a major predisposing factor in lameness caused by claw disorders.
The etiology of subclinical laminitis in cattle is not understood.
This causes gram negative organisms to die and release vasoactive endotoxins.
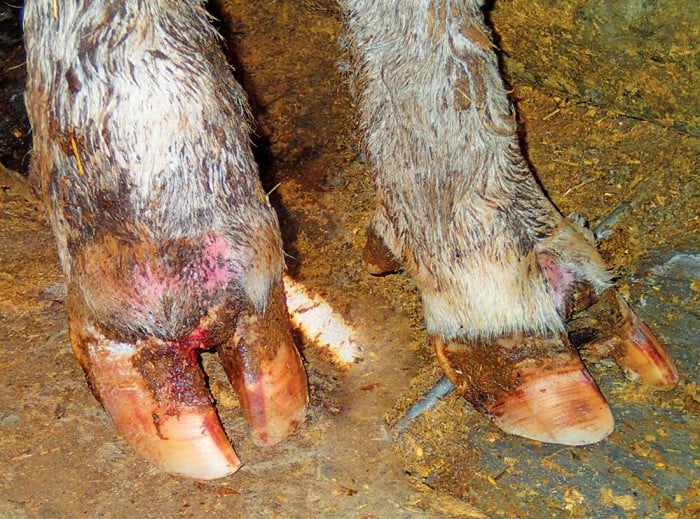
Dropped soles or flat.
Thus laminitis has a great economic impact on dairy operations and all over the world dairy producers are moving towards housing cows in intensive confined conditions.
Injectable diphenhydramine 0 5 to 1 0 mg kg iv im.
Recognizing and managing infectious causes of lameness in cattle.
Rings in hoof wall that become wider as they are followed from toe to heel.
Recognition of the disorder and management of the causative factors.
Bruised soles or stone bruises widened white line commonly called seedy toe with occurrence of seromas blood pockets and or abscesses.
Today laminitis also known as founder is the main cause of lameness in cattle.
Causes types of lameness toe tip necrosis.
The classic hypothesis suggests that high levels of carbohydrate in the diet see subacute ruminal acidosis invoke an increase of streptococcus bovis and lactobacillus spp which induce a state of acidosis in the rumen.
Speaking to a large crowd at the national cattlemen s beef association s cattleman s college in denver today tom edwards dvm kearney neb offered some tips on laminitis and responsible handling of downed cattle.
The bovine proceedings no 28 pp 71 74.
Laminitis can be caused by rumen acidosis.
Correct grain overload keeping the animal moving and the claws cool.
Nsaid non steroidal anti inflammatory drug injectable ketoprofen 2 to 4 mg kg im iv.
As we understand the causes of laminitis and identify the risk factors better it is possible to prevent and reduce the effects of the laminitis syndrome.
W hile it is associated with high concentrate feeding both laminitis and sole ulcers can be linked directly to.
Joint infections and arthritis.
Signs of chronic laminitis may include the following.